SYSTEM FOR MEASURING THE HETEROFORIA
|
Description |
This system allows the measurement of real heterophoria, the use of prisons or expensive optical equipment, looking for a more universal measurement. With this system you can achieve the highest precision and stability that exists with other standardized procedures in the diagnosis of binocular vision.
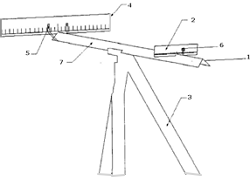
The invention comprises a bar of angular section that serves to support and has a millimeter scale on the sides, two options and two LED lights that can be moved on the angular bar, as well as a system for securing the elements and a tripod.
|
How does it work |
Description: Angular rod (1), near vision optotype (2), tripod (3), far optotype (4), far optotype clamping system (5), clamping system and fence optotype withdrawal (6) lateral scale (7)
The heterophoria is the physiological state or state of rest of the visual axes of both eyes that is measured, under usual conditions, when previously the fusion of the vision of the person evaluated has been dissociated or interrupted.
The latent deviation can be evaluated only when the person perceives the physiological diplopia on a line or with a dissociator of multiple forms. Any measurement of these methods is always subjective and depends on the ability of the specialist to get the most accurate data. This new system allows the measurement of real heterophoria, without the use of prisms or expensive optical equipment, looking for a more universal measurement.
The mentioned optotypes have stickers with scales in prismatic diopters with the zero in the center and a groove in the lower part, to ensure the placement of the zero just above the center of the profile of the bar. Two optotypes are placed, one at 40 cm and the other at 2 m, with the possibility of moving along the entire bar. Each optotype has an LED attached.
The measurement of the real heterophoria consists of evaluating the relative distance where the examined person sees double when it is fixed in one of the LEDs. To measure the heterophoria at a certain distance, the optotypes are placed at the point of light with a Maddox cylinder placed in the scanned patient's eyeglass, with a standardized clip, thus obtaining values of the different ocular deviations.
To do it more comfortably for the person being explored, it is advisable to put a red filter on either of the two eyes, in this way, the person scanned, with one eye sees red and with the other sees no color variation. Even if the person fixes his eyes on the LED, the bar is also included within his field of vision. Fixing the view on the LED you will see with each eye the profile of the bar separately and, thanks to the red filter, with each eye you will see the profile of the bar of one color, which will make it easier to distinguish one profile from the other. The two profiles of the bar that the person to evaluate sees while fixing the view on the LED intersect at a point, which is the point that should indicate the person we are evaluating to measure the difference with respect to the LED.
|
Advantages |
The main disadvantages of the measurement of heterophoria are the high prices, the great specificity of the commercial houses or of the equipment for their measurement, the subjectivity of the test and the conditions so different from the reality of the final result. This device, although it does not avoid the subjectivity of the test, eliminates the high costs, the difficulty of finding commercial houses that provide them and the disparity with reality.
|
Where has it been developed? |
The design, protected by national patent with previous examination since 2011, and its prototype, have been developed in the Faculty of Optics and Optometry.
|
Contact |
|
© Office for the Transfer of Research Results – UCM |
|
PDF Downloads |
|
Classification |
|
Responsible Researcher |
Ricardo Bernárdez Vilaboa: rbvoptom@ucm.es
Department: Optometry and Vision
Faculty: Optics and Optometry