Synergic effects of alloying elements in new stainless steels
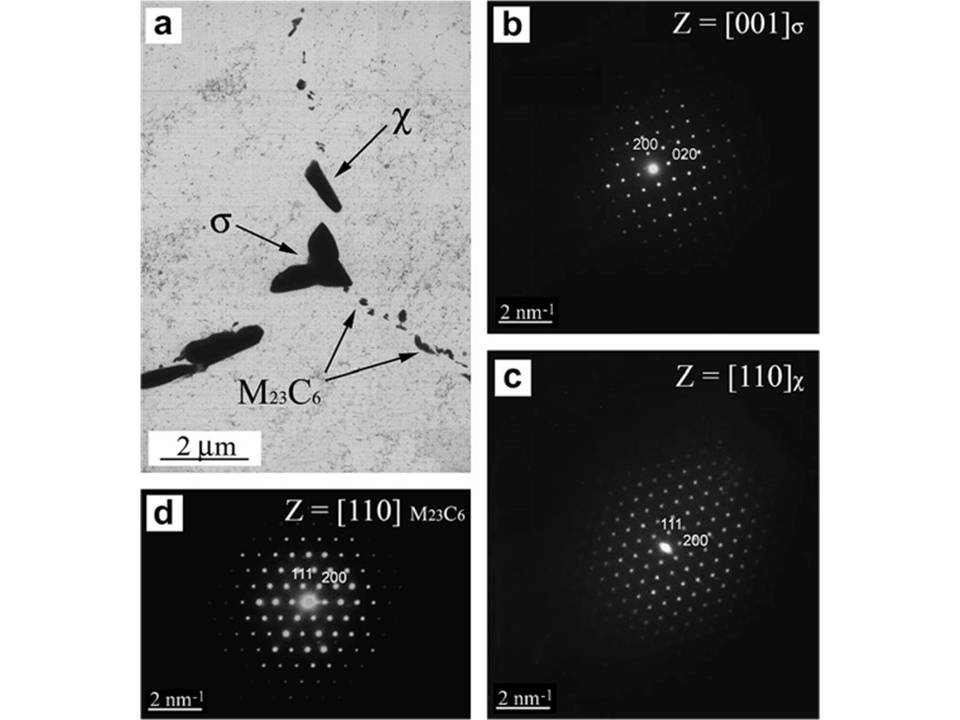
High corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steels is primarily attributed to the passive oxide film formed on its surface that, exposed to an aqueous solution, is a mixture of iron and chromium oxides, with hydroxide and water-containing compounds located in the outermost region of the film, and chromium oxide enrichment at the metal-film interface. However, the resistance of this passive film is determined by the environmental conditions which the stainless steel is exposed to, as well as by the alloy composition.
In this research line, the effect of alloying elements (Cu, Sn, Mn, Mo, Ti, C and N) on the corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steels is studied.