Nuevo artículo: Recovering urban nightlife: COVID-19 insights from Google Places activity trends in Madrid
tGIS y la Universidad de Kioto (Japón) presentan estudio sobre como se recuperó y cambió las actividades del ocio nocturno en Madrid a partir de datos de Google Places
30 jul 2024 - 14:25 CET
Autores: Enrique Santiago-Iglesias, Gustavo Romanillos, José Carpio-Pinedo, Wenzhe Sun, y Juan Carlos García-Palomares.
Resumen / Abstract:
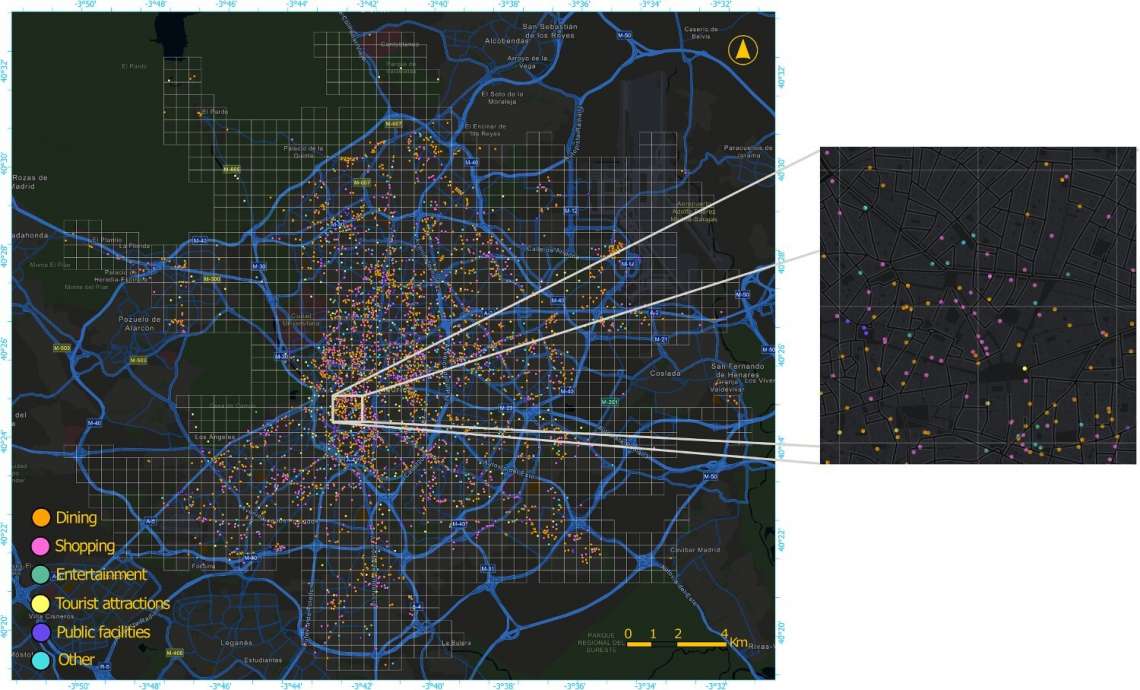
Nightlife in urban areas is gaining interest due to its role as a stimulus of the local economy, tourism, safety, and public services. However, most studies analyse nighttime activity from a qualitative perspective and at a general urban scale, without going into a detailed spatial analysis. In this paper, we have used the spatio-temporal details of Google Places data, and the activity trends at a variety of facilities that provide Google Popular Times. We studied and mapped the recovery of nighttime activity in the city of Madrid after the pandemic restrictions. The results reveal that there was a significant decrease of over 80% in the activity levels of open premises, which also led to a decrease in their average occupancy rate. These reductions were particularly noticeable in the city center and during the late-night hours.
Enlace: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/17445647.2024.2371927
¿Cómo citarlo? Santiago-Iglesias, E., Romanillos, G., Carpio-Pinedo, J., Sun, W., and García-Palomares, J.C. (2024). Recovering urban nightlife: COVID-19 insights from Google Places activity trends in Madrid. Journal of Maps, 20 (1). https://doi.org/10.1080/17445647.2024.2371927